An imo-neji is a machine element used to secure parts in position. In Japanese workplaces it may also be called a set bolt, hollow set (horo set), or retaining/set screw. It is a type of threaded fastener used for clamping and positioning components.
This page explains what an imo-neji is, where it is used, the different tip (point) styles, and the head/drive types.
What Is an Imo-Neji?
An imo-neji is a type of screw used for fixing and positioning machine parts. Besides “imo-neji,” it is also commonly referred to as a set screw or hollow set in Japan.
There are multiple drive types (such as internal hex and slotted), and many tip styles (flat point, cup point, etc.) selected based on the part being secured and the required holding method.
Common Uses of Imo-Neji (Set Screws)
The primary purpose of an imo-neji is to lock something in place. They are widely used—for example, to secure sprockets or pulleys to a shaft, or to fix handles and knobs to a component.
Example 1: Preventing a Sprocket Key from Sliding Out
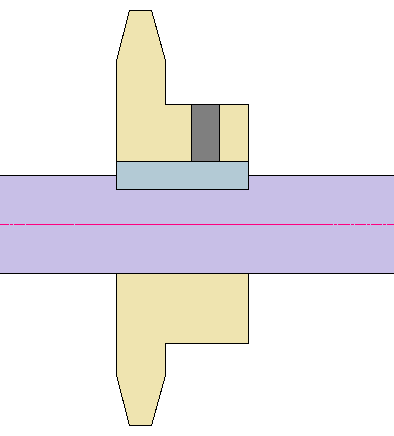
Set screws are often used to prevent the key between a sprocket/pulley (or other rotating component) and a shaft from backing out, and to minimize play and wobble.
Example 2: Anti-Rotation Locking for Bushings
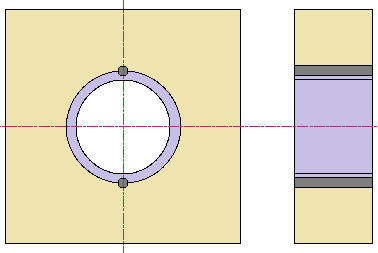
They are also used as anti-rotation locks for bushings, collars, and similar components.
Drive (Head) Types of Imo-Neji
Imo-neji come with several drive styles (how you apply tightening torque).
Hex Socket (Internal Hex)
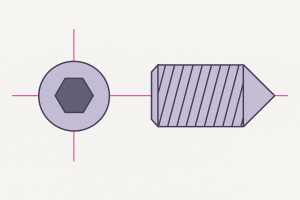
A set screw with an internal hex drive. Tighten using an Allen key/hex wrench.
Phillips (Cross Recess)

A set screw with a Phillips (cross) recess. Tighten using a Phillips screwdriver.
Slotted (Minus)
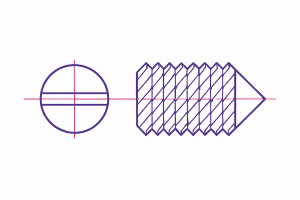
A set screw with a slotted drive. Tighten using a flat-blade screwdriver.
Torx
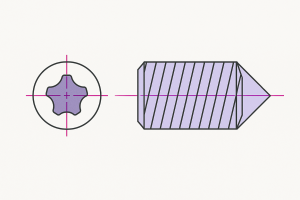
A set screw with a 6-lobe star-shaped Torx recess. Tighten using Torx drivers or Torx wrenches.
Tip (Point) Styles of Imo-Neji: Where They’re Used
Set screws have many tip geometries, chosen based on the application, the material being clamped, and whether the joint needs to be removable.
Cup Point
A cup point has a concave tip and is one of the most common styles. In Japan, “hollow set” often refers specifically to this cup point type.
Flat Point
A flat point is used where the screw may be adjusted repeatedly, or where you want to minimize damage to the mating surface.
Cone Point
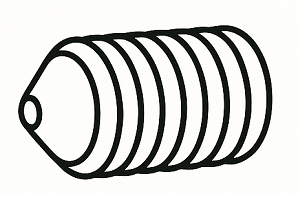
A cone point bites directly into the workpiece surface, providing strong holding power. It’s used where you want near-permanent locking or where loosening must be avoided.
Dog Point
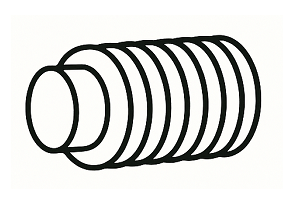
A dog point has a short cylindrical projection. It is used when the mating part has a drilled hole or clearance, and the projection can serve as a locating feature. In some setups it can act as a substitute for a key.
Oval Point
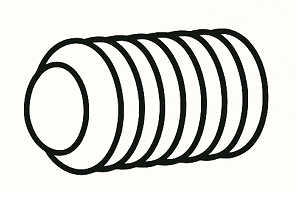
An oval point is used when the mating surface is not flat, helping maintain contact without digging in as aggressively as a cone point.
Other Names for Imo-Neji
Japanese (Common Synonyms)
- 止めねじ / 留めネジ (retaining screw / set screw)
- ホーローセット (hollow set)
- セットボルト (set bolt)
- セットスクリュー (set screw)
- 芋ねじ (imo-neji)
- 押しねじ (push screw)
- 虫ねじ (mushi-neji)
- イモビス (imo-bisu)
- セットビス / セットネジ (set screw / set “bisu”)
…and others.
English
- Set screw
- Hollow set screw (often used for cup-point types in some catalogs)
- Hexagon socket set screw / Hex socket set screw (for internal-hex drive types)
How Set Screws Are Specified (Including Size and Material)
A common way to specify a set screw is:
Material (finish/plating) + Tip style + Name/standard + Diameter × Overall length
Example 1
- Stainless steel
- Flat point
- Hex socket set screw
- Diameter: M6
- Overall length: 10 mm
Stainless Flat Point Hex Socket Set Screw M6×10
Example 2
- Black oxide
- Cone point (other options include cup point, etc.)
- Set bolt
- Diameter: M10
- Length: 15 mm
Black (Black Oxide) Cone Point Set Bolt M10×15
Note: Because black oxide is a very common finish for set screws, “black” (black oxide) is sometimes omitted in everyday naming.
Conclusion
Set screws (imo-neji) may look like “behind-the-scenes” parts, but they are essential machine elements—and they come in many variations.
By understanding the drive type and tip geometry, you can select the right set screw and apply it correctly for reliable locking and positioning.