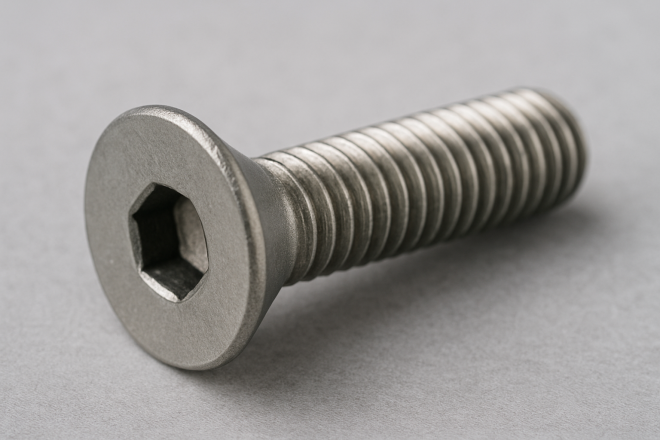
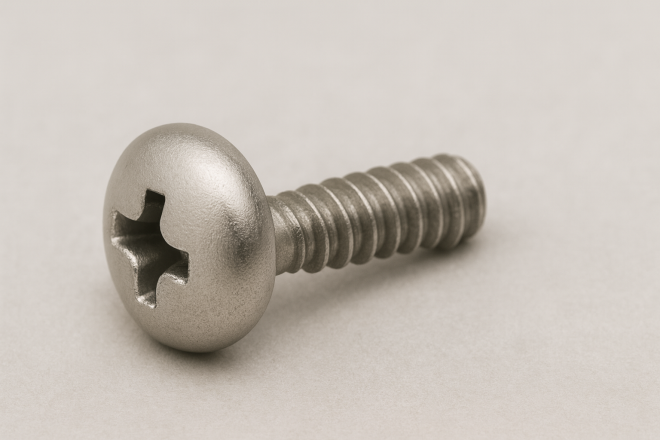
In Japanese manufacturing and DIY, you’ll often hear the words neji (screw/threaded fastener), bolt, and bisu (Machine Screws). They’re used interchangeably in daily conversation, but in practice there are clear differences in how each term is typically used.
This page explains the fundamentals: what “threads” really mean, how bolts differ from smaller screws, and what people usually mean by “bisu.” We’ll also cover representative types, their typical applications, and how their shapes affect installation and performance—useful for maintenance technicians, designers/engineers, and DIY users choosing the right fastener.
Screw vs. Bolt vs. “Bisu” (Machine Screws): What’s the Difference?
Here we clarify what each word usually means in the field, and how it’s commonly distinguished in Japanese usage.
What is a “Neji” (Threaded Fastener / Screw Thread)?

When people hear “neji,” many imagine familiar fasteners such as pan-head screws, countersunk screws, or hex-head bolts.
Technically, however, “neji” refers to anything that has a helical (spiral) thread form. Broadly, threaded components are classified into:
- Male threads (external threads): threads on the outside surface (e.g., bolts and screws)
- Female threads (internal threads): threads on the inside surface (e.g., nuts and tapped holes)
In other words, bolts, screws (“bisu”), and nuts are all types of threaded fasteners.
For nut types and shapes, see:
Nut Types, Shapes, and Features (18 varieties explained)
What is a Bolt?
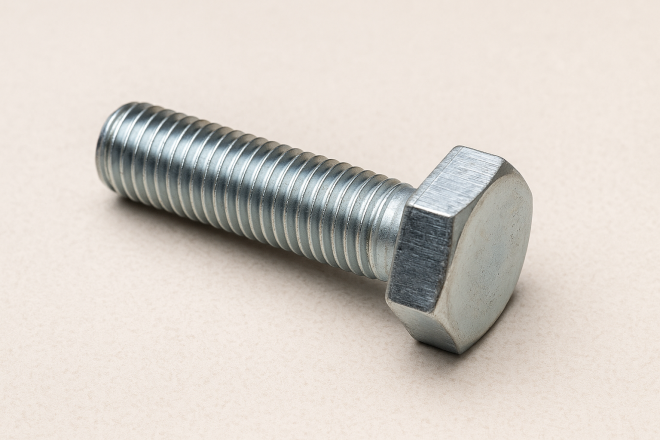

A bolt is one type of threaded fastener—specifically, a male-threaded fastener (external thread).
In many Japanese workplaces, “bolt” is commonly used to mean a fastener that:
- is typically larger than about 8 mm in diameter, and
- has a square or hex head (especially hex)
Note: In practice, there are many bolts under 8 mm, and many bolts with non-hex/square heads. For the variety of forms, refer to the bolt and screw types below.
What is “Bisu” (Machine Screws)?
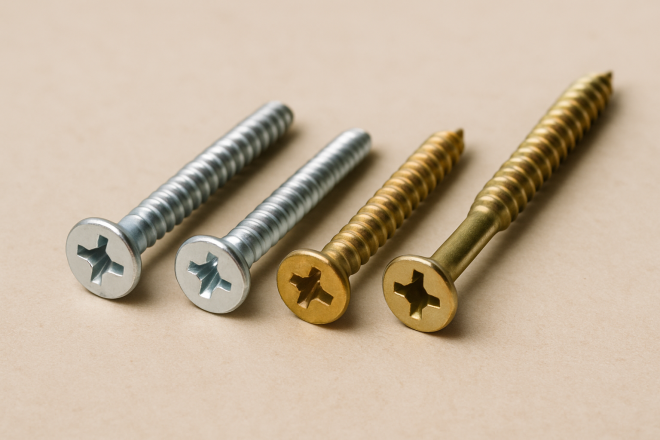

“Bisu” is commonly used to mean small screws—often what English would call machine screws or small diameter screws.
Typically, these are small male-threaded fasteners (about 1–8 mm) with a slotted or Phillips/cross recess so they can be tightened with a screwdriver.
Note: There are also “bisu” larger than 8 mm.
Additionally, in Japanese usage, the term “bisu” is often used for screws that do not require a pre-formed female thread—for example wood screws, coarse-thread construction screws, and drill-point/self-drilling screws that fasten directly into the workpiece.
Summary: Screw vs. Bolt vs. “Bisu”
Neji (Threaded fastener / screw thread)
A general term for items with threads; includes both male (external) and female (internal) threads.
Bolt
Commonly used for male-threaded fasteners with square/hex heads, often (in everyday usage) around 8 mm diameter and above.
“Bisu” (Machine screw / small screw)
A general term for smaller male-threaded fasteners with slotted or Phillips/cross recesses, typically under about 8 mm. When “bisu” appears in the product name, it often refers to screws that can be driven without a prepared female thread (depending on the type).
Common Bolt and Screw Types: Uses and Head/Drive Styles
Types of Bolts (Common Examples)
Hex Bolt (JIS B 1180)

A bolt with a regular hex head—often what people simply call a “bolt.”
It’s tightened using a spanner/wrench (or sometimes a socket). Because of its versatility, it’s widely used in everything from machinery to construction and general industrial applications.
Find sizes / purchase hex bolts here
Hex Flange Bolt with Captive Washer (JIS B 1187)

A hex bolt with an integrated washer set (typically a flat washer and spring washer) assembled so they won’t fall off.
The main advantage is improved work efficiency: you don’t need to separately handle or align washers, and it reduces the risk of forgetting washers or losing them during assembly.
Find sizes / purchase washer-assembled hex bolts here
Hex Socket Head Cap Screw (JIS B 1176)

A cylindrical head with an internal hex (Allen) drive. In Japan, it’s commonly called “hex socket bolt” or cap bolt; in English it’s typically “socket head cap screw.” You may also hear “socket screw” or “cap screw.”
It’s tightened with an Allen key/hex wrench.
Compared with hex-head bolts, which need wrench swing clearance, socket head cap screws can be tightened with minimal external clearance—useful inside machines, devices, and electrical enclosures where space is limited.
In recent years, they’re also used externally more often to take advantage of their strong clamping capability and clean appearance.
Find sizes / purchase socket head cap screws here
For a detailed breakdown of socket head variations, see:
Cap screw types: 8 socket-head styles explained
Button Head Socket Screw (Button Cap)
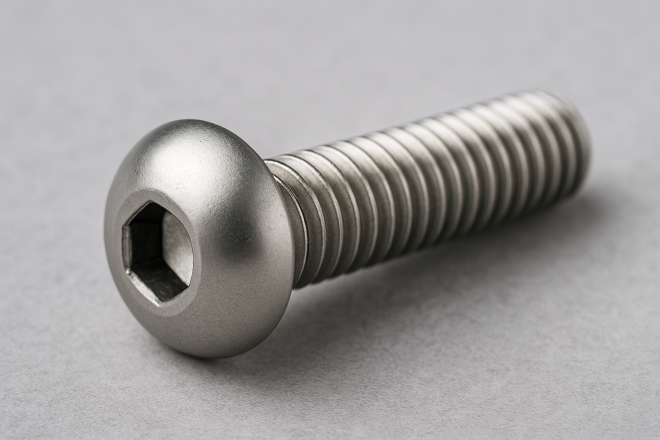

A socket screw with a rounded, low-profile head (often called “button cap” in Japan).
It’s commonly used where you don’t want the head to stand out. Because the head is smooth and less snag-prone (while still allowing strong tightening), it’s often selected for exposed areas of machines where hands may contact the surface.
Find sizes / purchase button head socket screws here
Countersunk Socket Screw (Flat Head Socket / “Sara Cap”)
A countersunk (flat) head with an internal hex drive. Like socket head and button head screws, it’s tightened with an Allen key.
Because the head sits flush when the mating surface is countersunk, it’s ideal where you want no protrusion—common for hinges and locations where clearance or appearance matters.
Find sizes / purchase countersunk socket screws here
Eye Bolt
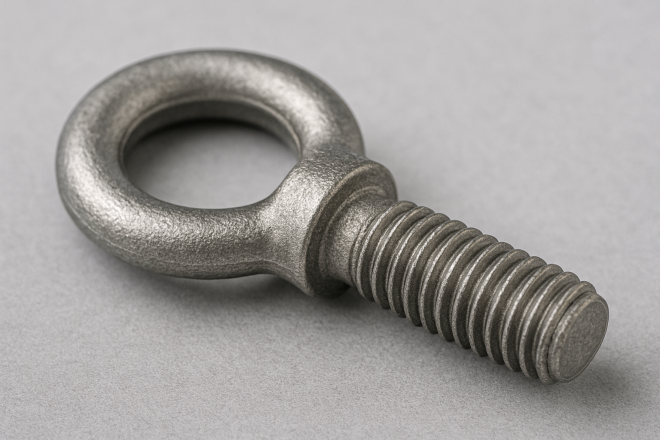

A bolt with a ring-shaped eye. It’s used to attach wire rope, slings, or lifting hooks for hoisting.
For machines and equipment with significant weight, eye bolts are frequently used during installation, handling, and relocation.
Find sizes / purchase eye bolts here
Wing Bolt (Butterfly Bolt / Wing Screw)
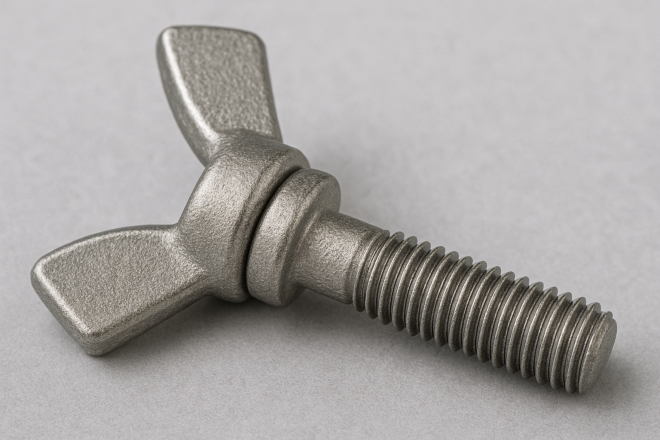

A bolt with wing-like “handles” for hand tightening. It’s also called a wing bolt or butterfly screw.
It can be tightened and loosened without tools, making it suitable for locations that require frequent adjustment or quick release.
Find sizes / purchase wing bolts here
U-Bolt
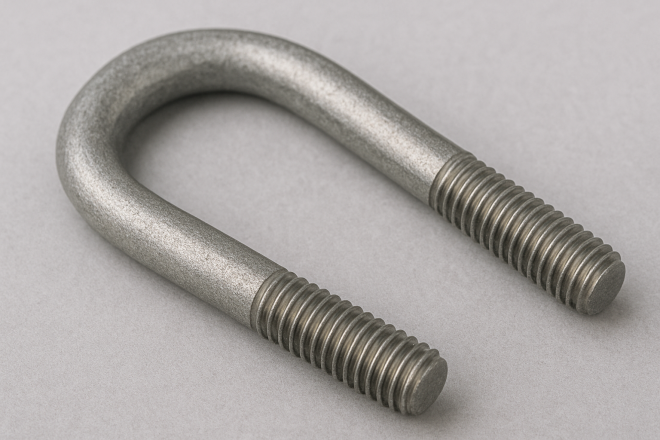

A U-shaped bolt with threads on both ends. Commonly used to clamp and secure piping.
Select the nominal size and standard to match the pipe you are fixing.
Find sizes / purchase U-bolts here
Leveling Bolt / Adjuster Bolt

A bolt with a swiveling pad at the tip used as an adjustable foot on floors. It allows height and level adjustment.
Common on machines, equipment, racks, shelves, and workbenches—anywhere stable leveling is required.
Find sizes / purchase leveling bolts here
Hex Socket Set Screw (Grub Screw / “Imo Neji” / “Horo Set”)
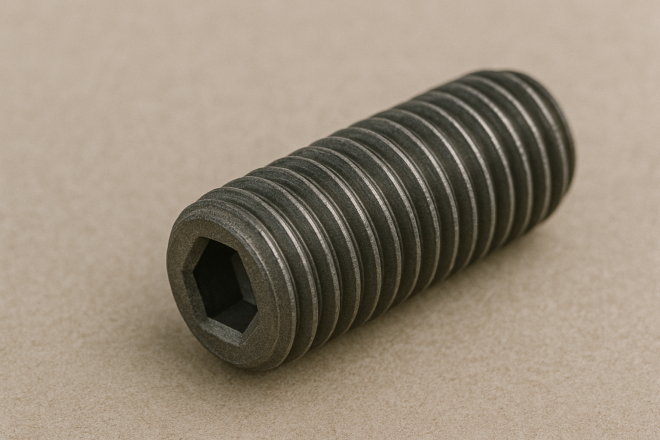

A headless screw whose outer diameter is essentially the same as the threaded portion, with an internal hex drive for tightening.
Often used as a machine element for fixing shafts, collars, pulleys, and similar parts. Because there is no protruding head, it’s commonly selected for rotating or drive mechanisms where safety and interference avoidance are important.
Find sizes / purchase set screws here
Anchor Bolt
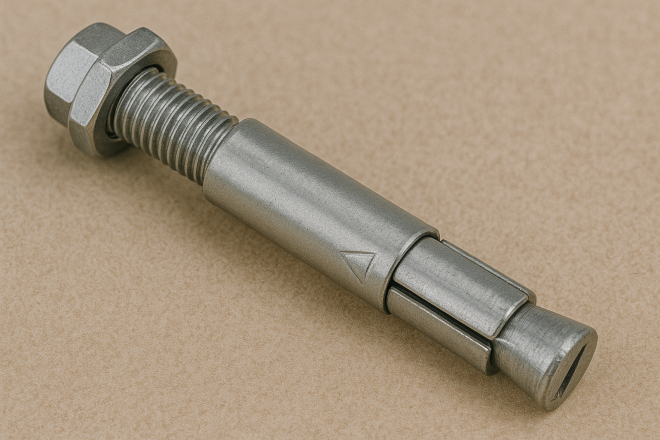

A bolt embedded in concrete so that the male thread protrudes above the surface. Used to fix machines and equipment to a concrete foundation.
Find sizes / purchase anchor bolts here
Timber Connector Bolt (“Hagoita Bolt”)
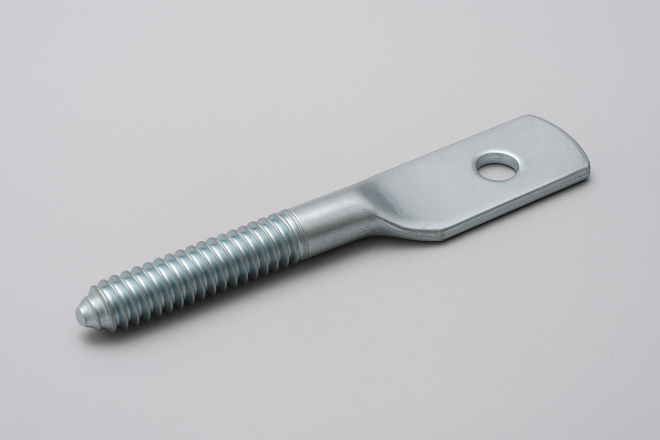

A bolt with a flat, plate-like head (resembling a “hagoita” paddle). It is used as a reinforcement fitting in building construction to help prevent beams from loosening or slipping out.
Find sizes / purchase timber connector bolts here
Stud Bolt
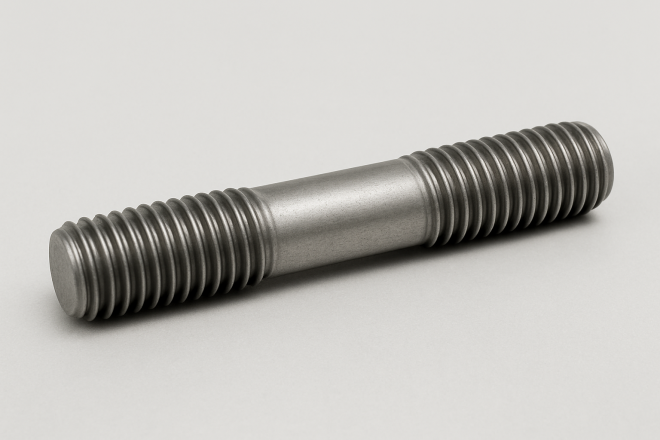

A bolt with male threads on both ends. Variations include fully threaded studs and studs threaded only at both ends.
Find sizes / purchase stud bolts here
Types of “Bisu” / Small Screws: Uses and Head Styles
Countersunk Machine Screw (Flat Head Screw)
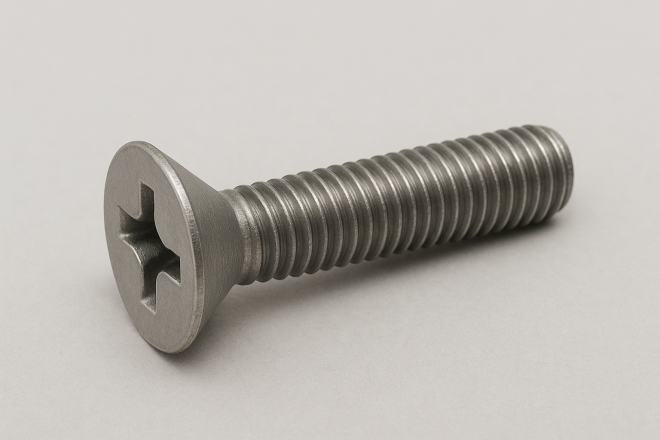
A machine screw with a countersunk (flat) head. In Japanese it may also be called “sara screw,” “countersunk screw,” or “flat head screw.”
By preparing a matching countersink in the workpiece, the head sits flush with the surface—useful for hinges and locations where a protruding head is undesirable.
Find sizes / purchase countersunk machine screws here
Pan Head Screw (Pan Head Machine Screw)

A pan head screw has a rounded head shape resembling the bottom of a pan. In many cases, when people casually say “screw,” they’re referring to this pan head style.
Because it’s widely applicable with no single dedicated use case, it’s one of the most general-purpose screws.
Find sizes / purchase pan head screws here
Truss Head Screw
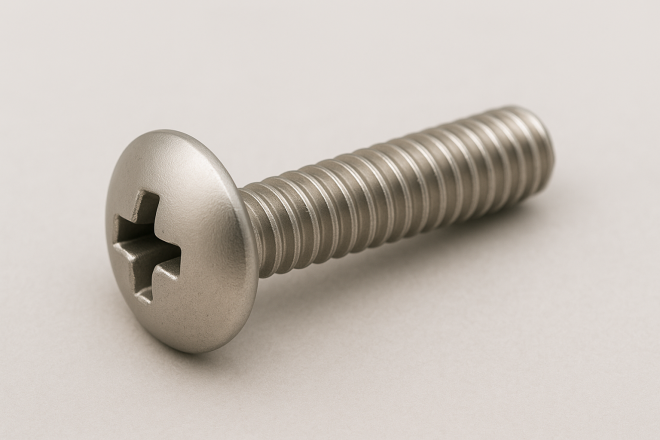

Similar to a pan head, but with a lower head height and a larger head diameter.
Because the head is low and broad, it’s often used where appearance matters or where you want more bearing area under the head.
Find sizes / purchase truss head screws here
Bind Head Screw
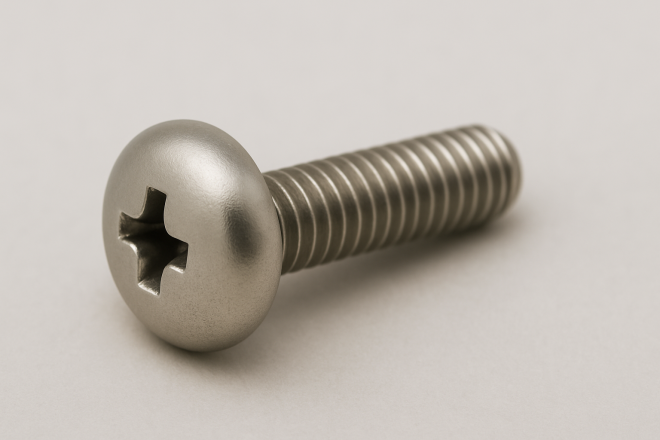

A rounded-head screw like pan and truss heads, but with a head diameter generally larger than pan head and smaller than truss head—often considered a “middle” profile between the two.
Find sizes / purchase bind head screws here
Washer-Integrated Screw (Captive Washer Screw)
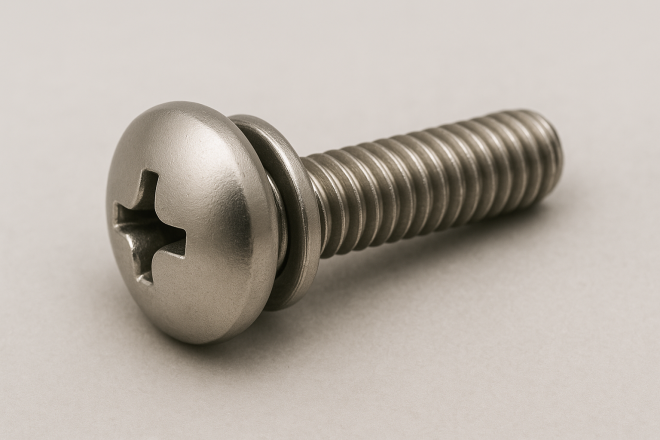

A screw with an integrated washer (captive washer).
It improves assembly efficiency by eliminating the separate washer handling step, reduces the chance of losing washers, and helps prevent washer omission.
Find sizes / purchase washer-integrated screws here
Tapping Screw
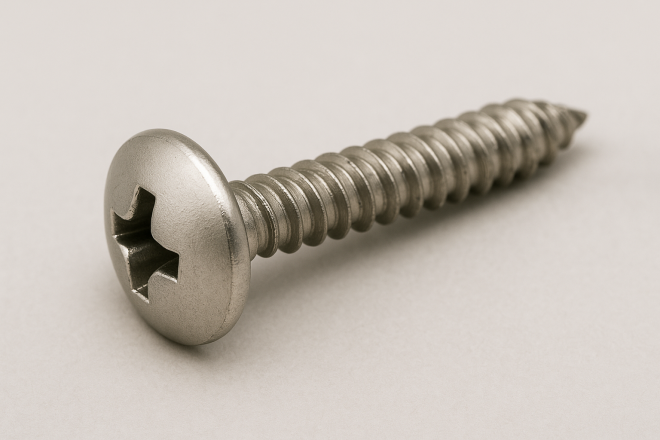

A screw that can fasten into a workpiece without a pre-cut internal thread.
For softer materials such as wood and plastics, it may be driven directly. For metal, it’s common to drill a pilot hole first and then drive the screw without tapping a female thread.
Find sizes / purchase tapping screws here
Hex Head Tapping Screw
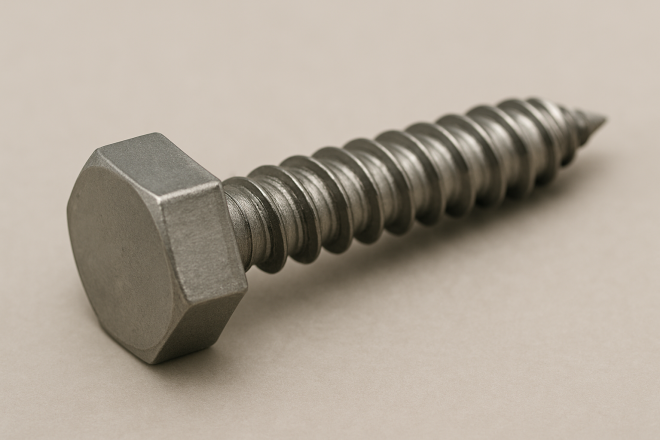
A tapping screw with a hex head, allowing tightening using a wrench or socket.
Find sizes / purchase hex head tapping screws here
Self-Drilling Screw (Drill Screw)
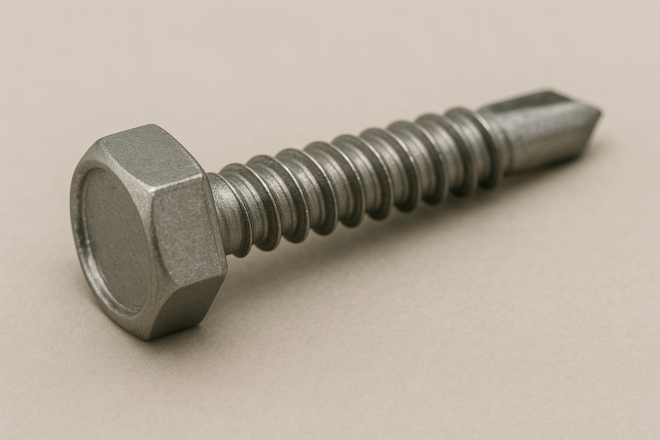

A screw with a drill-point tip. Because it can drill and fasten in one operation, it typically eliminates the need for a pilot hole depending on material and thickness.
Find sizes / purchase self-drilling screws here
Wood Screw
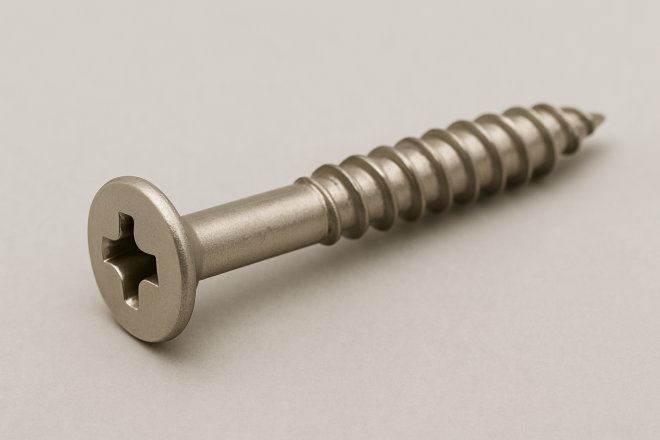

A screw designed specifically for fastening wood. Unlike some tapping screws, roughly the first portion of the shank is unthreaded (often around 30% of the length).
This helps prevent the clamped part from being “hung up” on threads, allowing the parts to be pulled tightly together and increasing clamping force.
Find sizes / purchase wood screws here
Interior/General-Purpose Construction Screw (“Multi-purpose Bisu”)
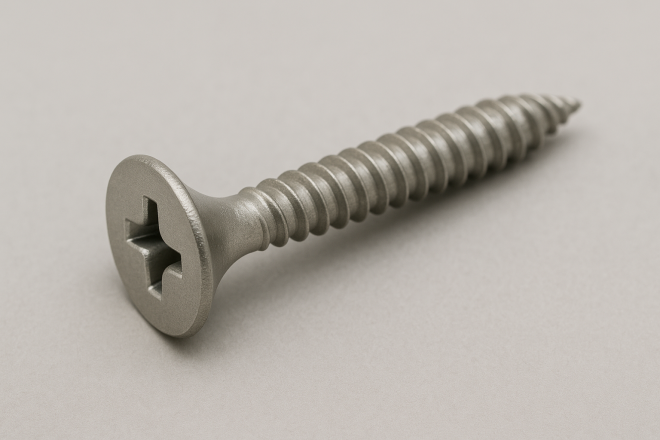

A general-purpose construction screw similar to wood screws. Commonly used for gypsum board, flooring, plastic boards, decorative tiles, and other materials—covering a wide range from softer to relatively harder substrates.
Find sizes / purchase interior/general-purpose screws here
Conclusion
Now that you’ve seen the differences between “neji,” bolts, and “bisu,” you can choose fasteners more confidently.
Selection depends on your application: the base material, required clamping force, whether you have a tapped hole or nut available, installation space, and the head/drive type you can access with tools.
Learn the main types, then select the bolt or screw best matched to your conditions.
For more bolt/nut fundamentals, also refer to: